Introduction
In Singapore, the national budget is shared with the public every year. It includes a revenue and expenditure report for the past financial year, covering revenue from taxes, fees and other charges. The expenditure makes transparent the operating and development cost of the Singapore Government.
This report is also forward-looking, providing expectations and the many initiatives planned that identify key priorities and focus areas for the government for the upcoming financial year. In this blog post, we explore Singapore’s 2022 Budget and discuss those areas that might impact, or might be an opportunity for the regulated industries in Singapore.
Given this context, please note that all monetary values are in Singapore Dollars ($), and all references and programmes are exclusive to Singapore-based entities unless otherwise noted.
2022 Budget Update
This year, digital capabilities are labelled a ‘first priority’ for the upcoming year with plans to spend $200 million to boost digital capabilities such as cloud adoption, cybersecurity, and automation. In addition, planned investments include increasing average broadband speeds and 6G to help businesses boost their digital infrastructure.
Small to Medium Enterprises (SMEs) will benefit most from the recent budget announcement, with existing initiatives such as the Advanced Digital Solutions (ADS) initiative and the Productivity Solutions Grant (PSG) being expanded to provide more funding to eligible organisations.
The Future Economy Council (FEC), responsible for driving Singapore’s growth and transformation roadmap, introduced Industry Transformation Maps (ITM) before the COVID-19 pandemic to map out areas that can help drive growth in various industries such as manufacturing and modern services.
Sub-committees assigned by the FEC are responsible for implementing groups of ITMs across similar industries – called ITM Clusters. There are currently seven ITM Clusters that target different areas of the economy. The Cluster most relevant to Sourced and the industry we work in is the Modern Services Cluster, which oversees Information and Communication Technology (ICT) & Media, Financial Services and Professional Services.
More information on the different clusters can be found here.
The upcoming measures to boost Singapore’s digital infrastructure show the Singapore government’s commitment to digital transformation.
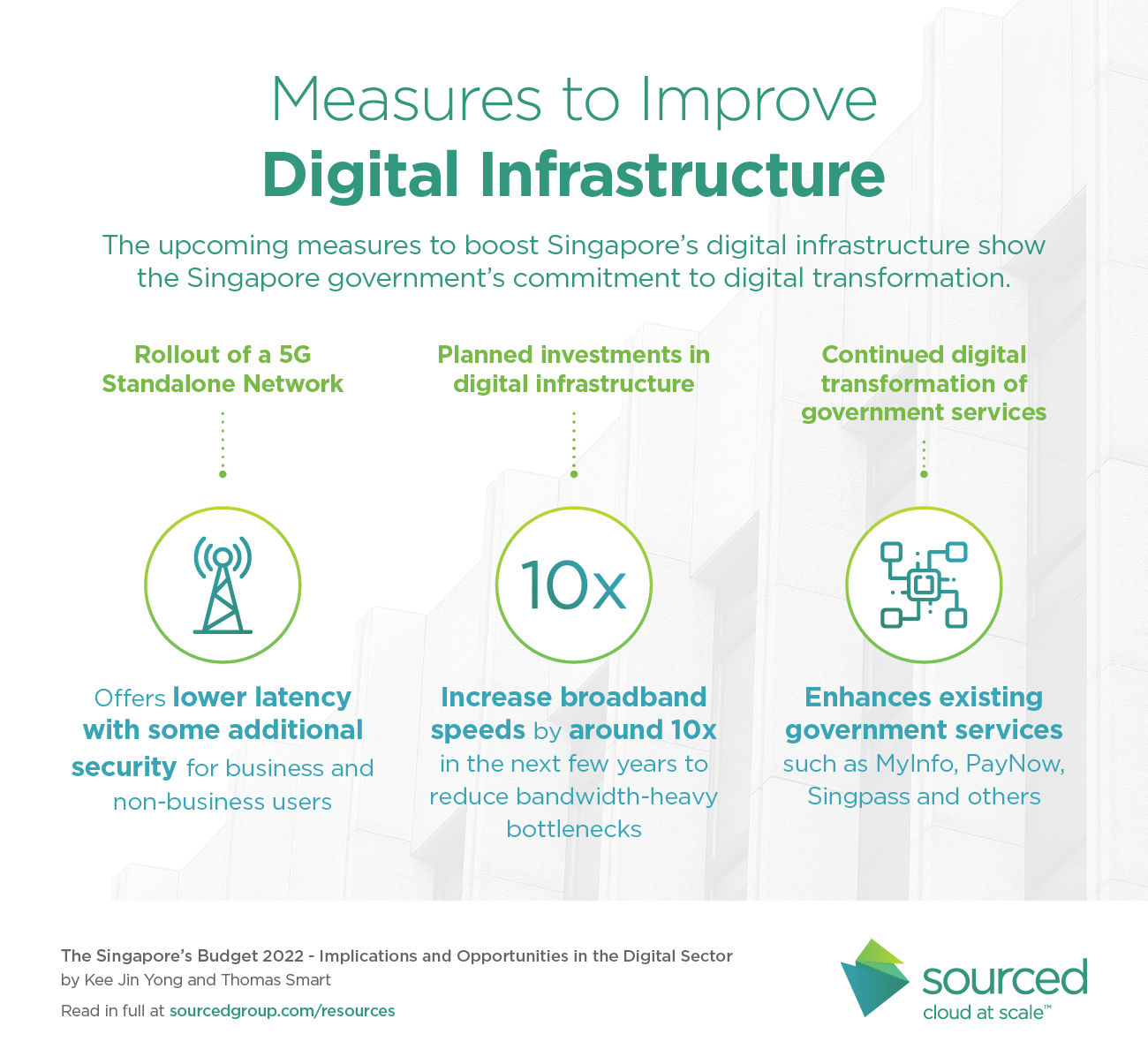
1. Rollout of a 5G Standalone Network
A 5G Standalone network (5G SA) uses independent signals to transmit data. Previously, some of the signals transmitted might partially rely on the existing 4G LTE network components (5G Non-SA). While the 5G Non-SA and SA networks can be used alongside each other, the most innovative and cutting-edge use-cases for 5G require a standalone network. Standalone networks provide lower latency and some additional security. Singtel, one of the major telcos in Singapore, announced the launch of its 5G SA network in May 2021.
For businesses that want portable access to 5G, Singtel launched a 5G platform called GENIE in April 2021.
For more information about GENIE.
2. Planned investments in digital infrastructure
- Increase broadband access speeds by around ten times in the next few years.
According to the Speedtest Global Index, as of March 2022, Singapore ranks 2nd globally with the median fixed broadband speed at 194Mbps – https://www.speedtest.net/global-index - Communications technology is another key area for government focus, with significant investments in capabilities such as 6G. It was noted in the Budget that while newer technologies such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) were not directly included, part of the digital strategy is to explore how these technologies might evolve with higher network speeds available to them.
- Organisations can benefit from the higher speeds and lower-latency networks. Bottlenecks with applications that are bandwidth-heavy can be eliminated. With the rise of digitally-enabled services such as mobile banking and payments, the investments in digital infrastructure will enable more customers to gain near real-time access to these services. For the applications, high speeds provide an opportunity to increase the quality and amount of content.
3. Continued digital transformation of government services
New integrations and additional features will be added to enhance existing government services such as MyInfo, PayNow and SingPass, and there are upcoming plans to develop new applications to provide secure and convenient access to additional digital government services and data.
Opportunities for Organisations
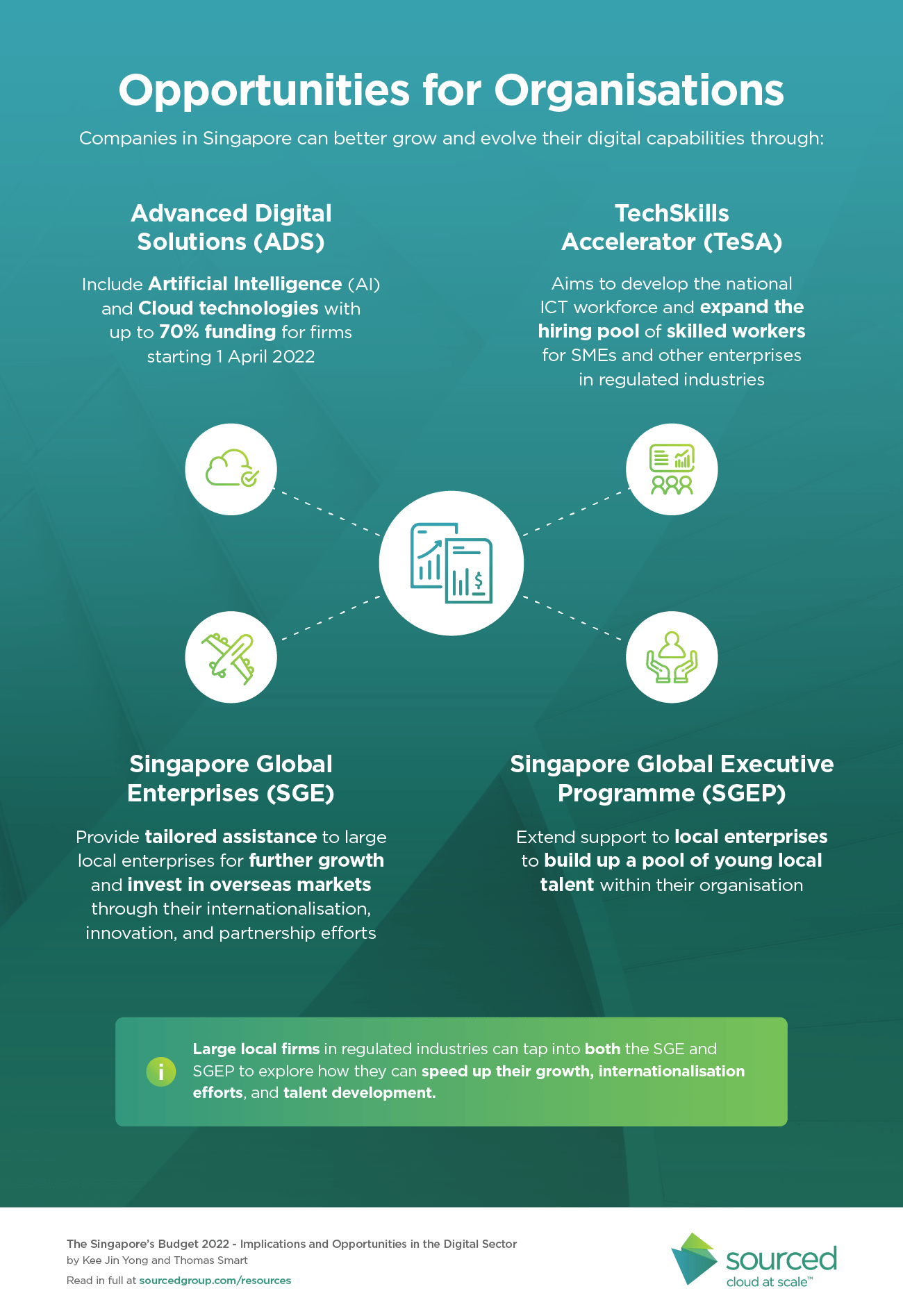
The following are just some of the key initiatives that can make it easier for companies in Singapore to grow and evolve their digital capabilities.
1. Advanced Digital Solutions (ADS)
- ADS was put in place in 2020 to increase the adoption of advanced technologies and integrated solutions, including robotics, IoT and Blockchain. Such technologies can potentially help mitigate challenges that organisations might face, such as with e-payments or inventory management.
- From 1 April 2022, ADS will be expanded to include solutions that use Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cloud technologies to help organisations improve operational efficiency and business decisions. Previously, AI and Cloud were not on the pre-approved list of solutions under the ADS. The complete list of supported IMDA projects can be found here
- Up to 70% funding of solutions such as cloud when firms participate in this initiative. The funding covers these areas:
- Hardware, software, infrastructure, connectivity, cybersecurity, integration, development, enhancement and project management
- Deployment of solutions (e.g., acquisition, subscription, lease, transaction, training and professional services like programmers and project managers)
- Organisations can start by exploring the list of approved projects and contact the leads of the projects for more information. Organisations can expect to see more projects added this year that use technologies involving cloud and AI.
- The enhanced scope of ADS will also benefit firms looking to the cloud to host their workloads and wanting to leverage funding to support these efforts.
2. TechSkills Accelerator (TeSA)
- TeSA is led by IMDA in partnership with Skillsfuture Singapore (SSG) and Workforce Singapore (WSG). SSG is a statutory board under the Ministry of Education (MOE), which aims to promote a culture of lifelong learning through mastery of skills. WSG is responsible for transforming the current workforce to meet Singapore’s economic needs. TeSA aims to grow and develop the national ICT workforce and is helpful for organisations looking to hire and upskill ICT talent.
- Over 120,000 individuals have been trained as a part of this programme, including specialised technical skills such as cybersecurity and AI.
- Placement programmes have been widely successful, with 12,000 individuals placed in ICT related jobs since the programme’s start. The 2022 Budget statement stated that TeSA would be expanded to include upskilling of mid-career workers:
- Partnering with industry leaders to grow product development teams in Singapore
- Expanding TeSA to SMEs and start-ups to provide more job opportunities for mid-career workers
- Bolstering the skills of our current digital workforce to keep their skills relevant to the needs of the industry
- A myriad of programmes to support ICT and non-ICT professionals in upskilling and obtaining domain knowledge that is high in demand today and is expected to remain so for the foreseeable future.
- SMEs in regulated industries can expect a larger hiring pool of skilled workers. Businesses can look to employ mid-career workers who have already undergone the relevant training from TeSA for both entry-level and specialist technical roles.
More information about TeSA can be found here.
3. Singapore Global Enterprises (SGE) & Singapore Global Executive Programme (SGEP)
- The SGE and SGEP were newly announced schemes during this year’s budget statement.
- SGE aims to provide tailored assistance to large local enterprises, helping them to increase in scale and allowing them to invest in overseas markets.
- There are four ways where support will be provided, which focus mainly on internationalisation, innovation and facilitating partnerships with other organisations:
- Developing globally ready executives
- Setting up new business ventures
- Facilitating mergers and acquisitions
- Facilitating better access to financing
- Singapore Global Executive Programme (SGEP) was launched to extend support to local enterprises, allowing firms to build up a pool of young local talent within their organisation. It provides enterprises with knowledge from more experienced enterprises in their domain area. At the same time, assistance can be provided through partnerships to improve their attractiveness as employers. Lastly, resources will also be offered to organisations to build an in-house HR team, which will enable them to start building talent development initiatives.
- Large local firms in regulated industries can tap into the wealth of support from both the SGE and SGEP to explore how these schemes can help speed up their growth and internationalisation efforts and, at the same time, develop their own pipeline of talent.
More information about the Singapore Global Enterprise (SGE) initiative can be found here.
Opportunities in the Cloud
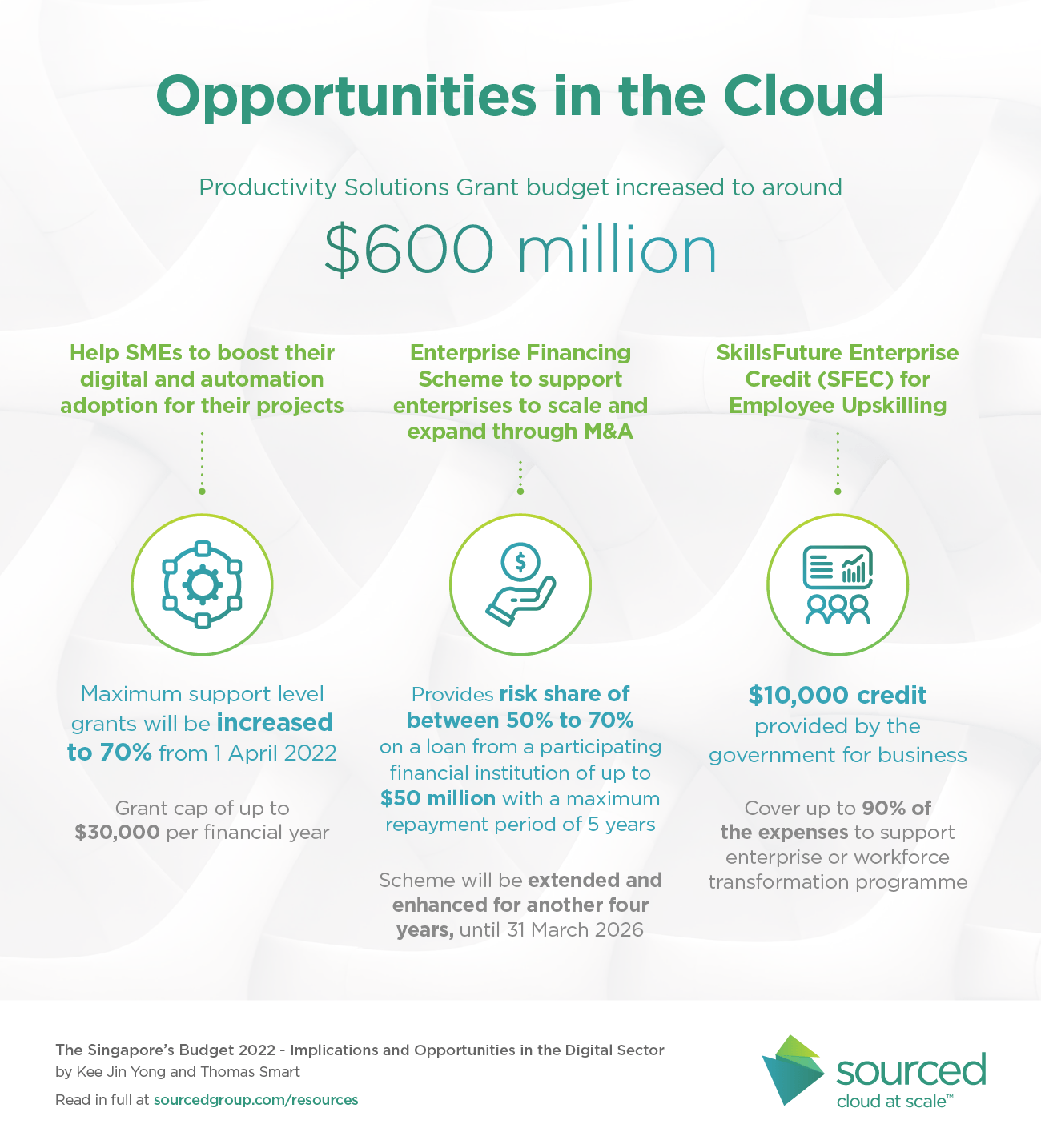
1. Productivity Solutions Grant budget increased to around $600 million
- This is to boost SMEs to undertake projects that involve digital and automation solutions
- Companies who are interested in adopting IT solutions/equipment to boost their business processes are eligible
- The maximum support level for grants will be increased to 70% from 1 April 2022
- The figure has doubled since the scheme was first launched four years ago
- Grant cap of up to $30,000 per financial year
- https://www.enterprisesg.gov.sg/financial-assistance/grants/for-local-companies/productivity-solutions-grant
- https://www.gobusiness.gov.sg/productivity-solutions-grant/
2. Enterprise Financing Scheme – Merger & Acquisition (M&A)
- Supports enterprises to scale and expand through M&A
- The scheme provides risk share on a loan from a participating financial institution of up to $50 million with a maximum repayment period of 5 years. The interest rate is based on the financial institution’s assessment.
- The risk share is 50%. For young enterprises or those in a challenging market, the risk share may be 70%.
- If the financial institution is unable to recover the loan, they can make a claim against Enterprise Singapore for the unrecovered portion of the risk share.
- This scheme will be extended and enhanced for another four years, until 31 March 2026.
- Support for domestic M&A activities has been added.
Employee Enablement
1. SkillsFuture Enterprise Credit (SFEC)
- $10,000 credit provided by the government for businesses
- This helps to cover up to 90% of the expenses to support enterprise or workforce transformation programmes
- It enables companies to train workers and for individuals to improve their skills in in-demand areas
Measures for Individuals
The government provides funding for mid-career individuals looking to pick up skills that are high in demand:
- SkillsFuture Career Transition Programme (SCTP)
- SGUnited Mid-Career Pathways Programme – Company Attachment (SGUP-CA)
Conclusion
Given the sheer number of announcements and initiatives in the 2022 Budget to help boost Singapore’s digital capabilities, there is no better time for organisations in Singapore to embark on their cloud journey and digital transformation. The budget and support from the government can help organisations cover some of the costs and reduce barriers. By identifying the most relevant initiatives, you can find those that offer your organisation the greatest impact and the most value.
More information and the full Budget 2022 report can be found here.





